|
Overview
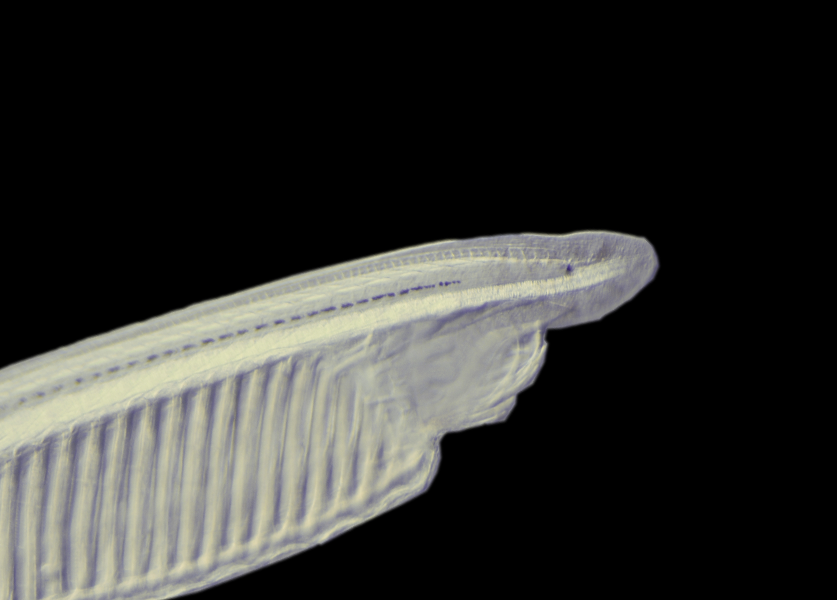
 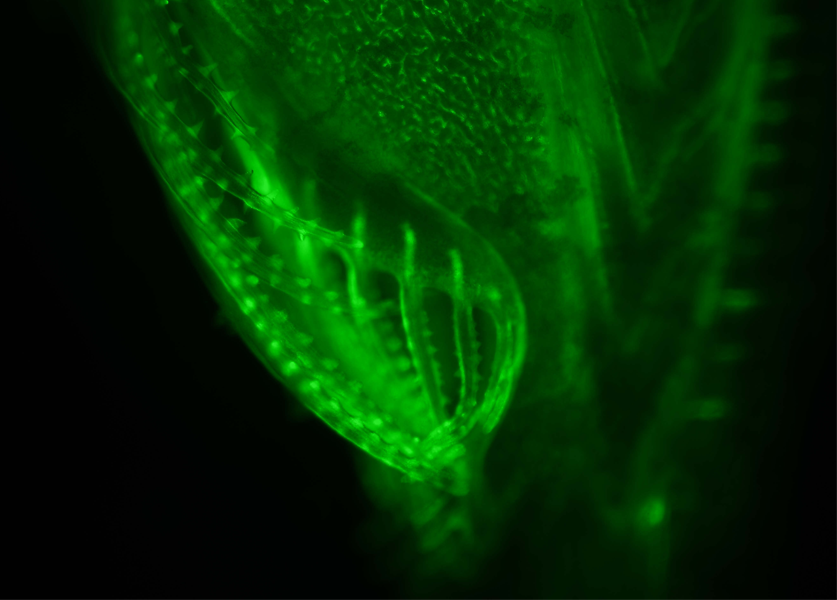
Interest The phylogenetic position of amphioxus, together with its relatively simple and evolutionarily conserved morphology and genome structure, has led to its use as a model for studies of vertebrate evolution. In particular, recent development of technical approaches, as well as access to the complete amphioxus genome sequence, for the Mediterranean amphioxus, Location: Mediterranean Sea and North-East Atlantic Attractive features
Contributions Studies with different amphioxus species have helped answer questions about the evolution of the chordate genome, and particularly the evolution of the Hox cluster structure and cis-regulatory elements, the evolution of the control of axial patterning in chordates, and the appearance of vertebrate-specific structures such as the head. Tools
Drawbacks Due to a short spawning period (May-July), in vivo experiments are restricted to a short period only. Their life cycle is also relatively long, about 2 years to reach adulthood, and no knockdown techniques are available (no morpholinos, RNAi or siRNA). Selected references
Transcript Browser
The following browser provides a quick view for new visitors. Use the searching mechanism to find specific features.
Pages |


